Variability in reaction time
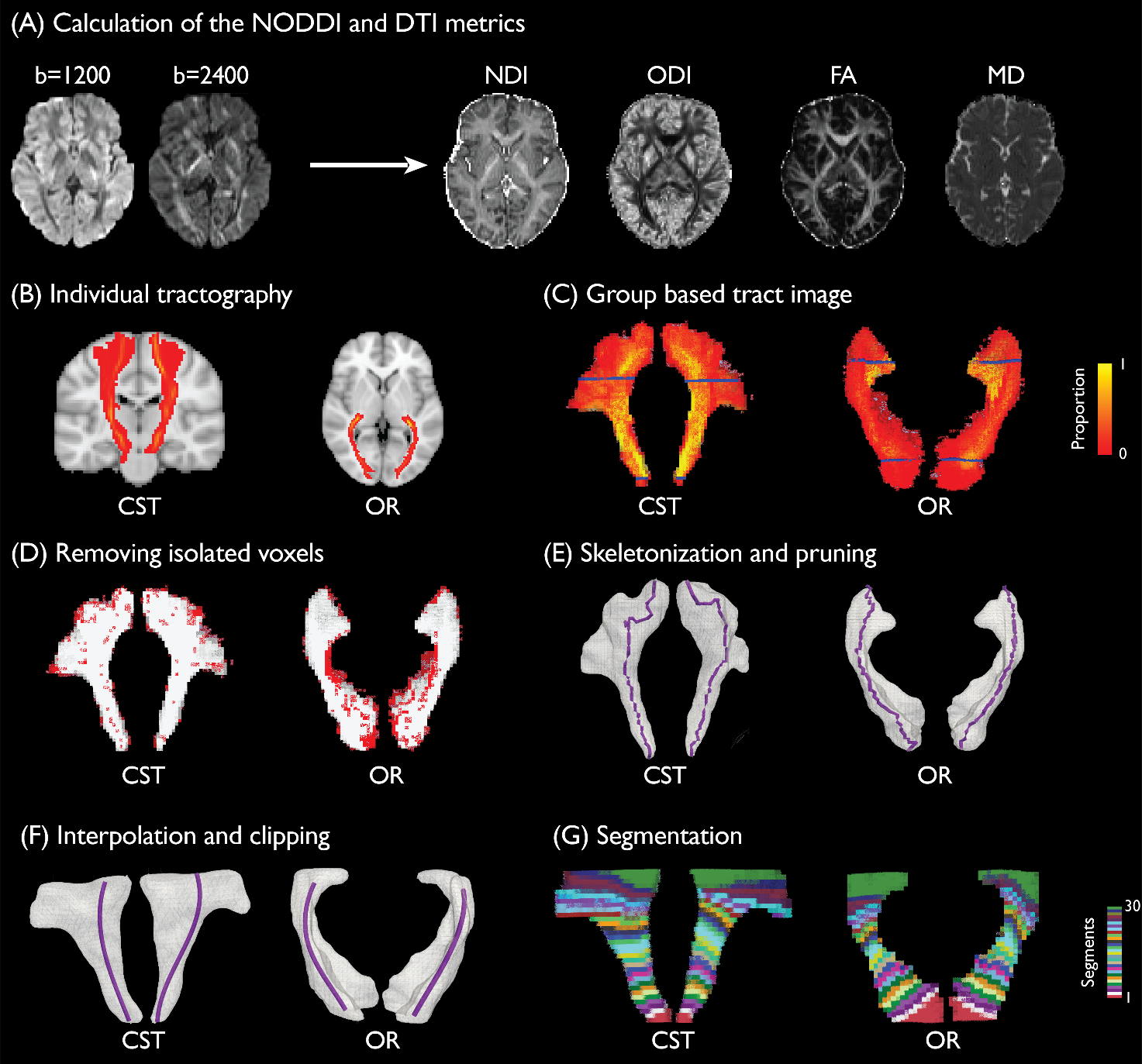
The speed of voluntary reaction to an external stimulus varies substantially between individuals and is impaired in ageing. However, the neuroanatomical origins of inter-individual variability in reaction time (RT) remain largely unknown. We combined a cognitive model of RT and a biophysical compartmental model of diffusion-weighted MRI to characterize the relationship between RT and microstructure of the cortico-spinal tract (CST) and the optic radiation (OR), the primary motor output and visual input pathways associated with visual-motor responses.
Related publication: Cognitive and White-Matter Compartment Models Reveal Selective Relations between Corticospinal Tract Microstructure and Simple Reaction Time